It shows a quick response against pathogens. Chapter 21 - The Immune System.
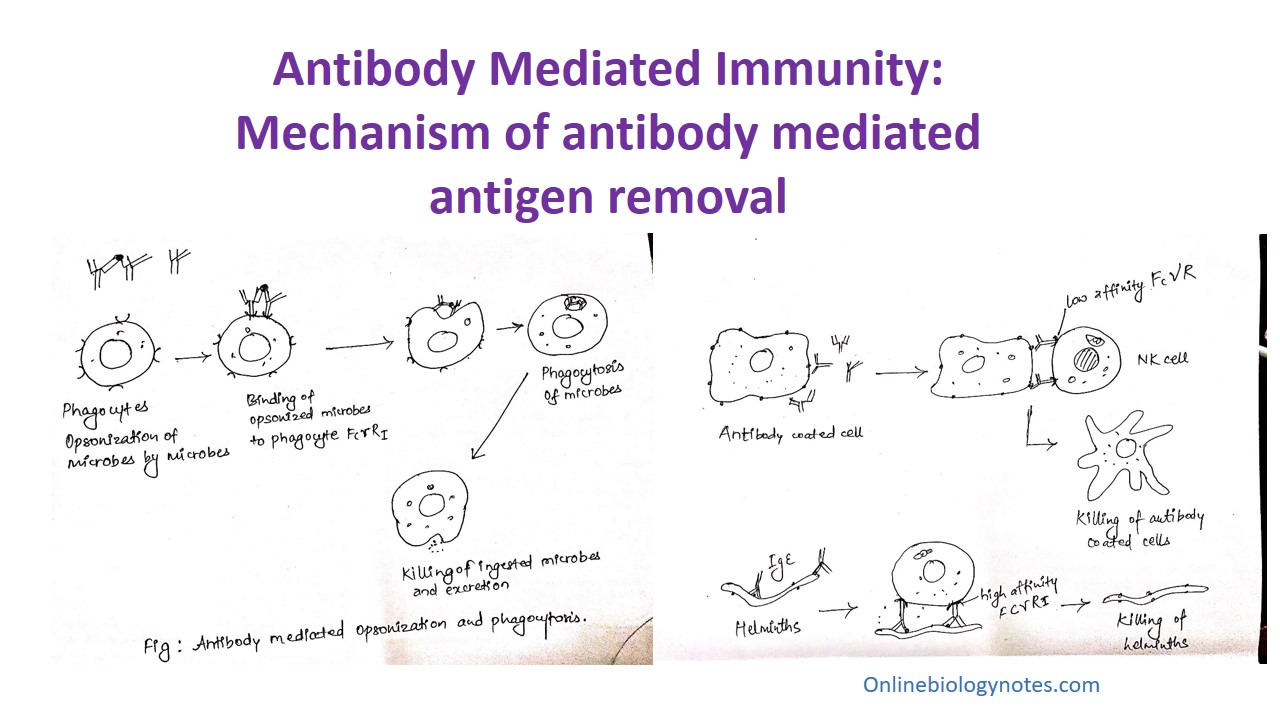
Antibody Mediated Immunity Ami Activation And Mechanism Of Antibody Mediated Antigen Removal Online Biology Notes
Antĭ-bode an immunoglobulin molecule having a specific amino acid sequence that gives each antibody the ability to adhere to and interact only with the antigen that induced its synthesis.

. Mechanisms of the immune system. - Antibodies are produced by a subset of lymphocytes called B cells. Try this amazing Immune System Chapter 21 quiz which has been attempted 5661 times by avid quiz takers.
Nanocapsules have been found to be viable adjuvants and are amenable to engineering for desired immune responses. Mucosal immunity immunopathology 6. A Antibody-mediated immunity is called humoral immunity because it is mediated by antibodies macromolecules in the extracellular fluid complement proteins present in the blood.
Active Immunity results when exposure to a disease organism triggers the immune system to produce antibodies to that disease. 1 neutralization prevents antigen eg virus toxin from functioning 2 agglutination the cross-linking of antigens into a large complex 3 opsonization enhancing the process of phagocytosis 4 antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity facilitating destruction of eukaryotic pathogens. The enormous diversity of antibodies specific for distinct viruses pathogens and many other antigens is explained by clonal selection whereby specific B-lymphocyte receptors recognize a particular antigen.
Once the first protein in the pathway is turned on the following complement proteins are called into action with each protein turning on the next one in line. Among these IgA1 is highly found in the secretions and is also called the secretory immunoglobulin. The active serum components were identified to be immunoglobulins Igs called antibodies.
It constitutes 13 of the total antibody content in the serum and is divided into 2 sub-classes- IgA1 and IgA2. Also referred to as antibody-mediated immunity humoral-mediated immunity involves substances found in the humor or body fluids. The measurement of antibodies specific to COVID-19.
It exists in both monomeric as well as dimeric forms. In vivo tests eg delayed type hypersensitivity skin reaction and tetanus antibody production confirm the polarization of the adaptive immune response towards the TH2 pathway. Regulation of immunity the microbiome 7.
We previously showed that natural nanocapsules called vaults can be genetically engineered to elicit Th1 immunity. Humoral immunity is the aspect of immunity that is mediated by macromolecules - including secreted antibodies complement proteins and certain antimicrobial peptides - located in extracellular fluids. Inflammation autoinflammation 9.
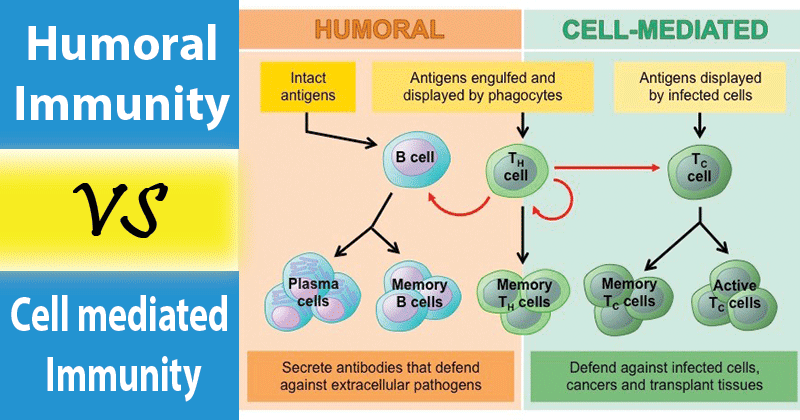
There are two types of immunity. The development of immunity to a pathogen through natural infection is a multi-step process that typically takes place over 1-2 weeks. B cell activation by helper T cells Antibody production by plasma cells Destructionelimination of target antigen-antibody complex.
Also explore over 36 similar quizzes in this category. In contrast IL-10 and transforming growth factor-beta essential to TH2-mediated humoral or anti-inflammatory immune response are upregulated. Antibody-mediated immunity involves B cells and the production of antibodies in response to a specific antigen.
It is also called antibody-mediated immunity. Modifications of adjuvants that induce cell-mediated over antibody-mediated immunity is desired for development of vaccines. Humoral immunity is the immunity mediated by macromolecules present in extracellular fluids.
This antigen-specific property of the antibody is the basis of the antigen-antibody reaction that is essential to an immune response. The steps involved in the process are. Humoral immunity is named so because it involves substances found in the humors or body fluids.
2012 Farlex Inc. These antibodies have evolved to target different antibodies. With assistance from helper T cells B cells will differentiate into plasma B cells that can.
Helper T cells also control isotype switching and have a role in initiating somatic hypermutation of antibody variable V-region genes molecular processes that were described in Chapter 4Figure 91The humoral immune response is mediated by antibody molecules that are secreted by plasma cellsAntigen that binds to the B-cell antigen receptor. Which of the following best describes the immunity gained from a vaccine. Antibody-mediated immunity definition immunity conferred to an individual through the activity of B cells and their progeny which produce circulating antibodies in response to the presence of a foreign substance and recognize the substance upon renewed exposure.
Extracellular fluid is the fluid present outside the cells of a multicellular organism. Antibody-Mediated Humoral Immunity Involves production of antibodies against foreign antigens. B In vaccination a preparation of antigenic proteins of pathogen or inactivatedweakened pathogen vaccine is introduced into the body.
An immunoglobulin produced by plasma cells which has a specific amino acid sequence and specifically binds to the antigen s eg foreign proteins microbes or toxins that induced its synthesis. Humoral immunity is mediated by antibodies. This range of antibody activities provides a response to rapid antigen-specific B cells production during infections.
The body responds to a viral infection immediately with a non-specific innate response in which macrophages neutrophils and dendritic cells slow the progress. Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses 100 200 300 400 500 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 Phagocytes Inflammation The Adaptive Immune System Humoral Immunity Cell-Mediated Immunity FINAL ROUND. Cell mediated immunity 18.
Antibodies are also called immunoglobulins. What type of immunity is responsible for agglutination of viruses. Cell-mediated immunity is an immune response that does not involve antibodiesRather cell-mediated immunity is the activation of phagocytes antigen-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocytes and the release of various cytokines in response to an antigen.
Answers 1 P Priyanka Kumari. The binding of antibody to antigen. T cell mediated autoimmune diseases 10.
It provides the first line of defence against the pathogens and limits inflammation. Antibody-Mediated Humoral Immunity. Antibody-mediated immune mechanisms Protective attachment to antigens.
Epigenetics modulation of immunity 8. Antibodies may also bind to closely related antigens. External barriers to infection.
It is the major defence mechanism against extracellular microbes trying to invade the host systems. It contrasts with cell-mediated immunity. It is one of the mechanisms of the active immune system associated with circulating antibodies.
Active immunity can be acquired through natural immunity or vaccine-induced immunity. Humoral immunity is also called antibody-mediated immunity. Humoral immunity is also.
The antibodies produced by the B-cells bind to the antigens and neutralize the microbes.

Antibody Mediated Inflammatory Disorders
0 Comments